Electric Vehicles in India: 7 Strong Signals of a Historic Automobile Transformation
4 min read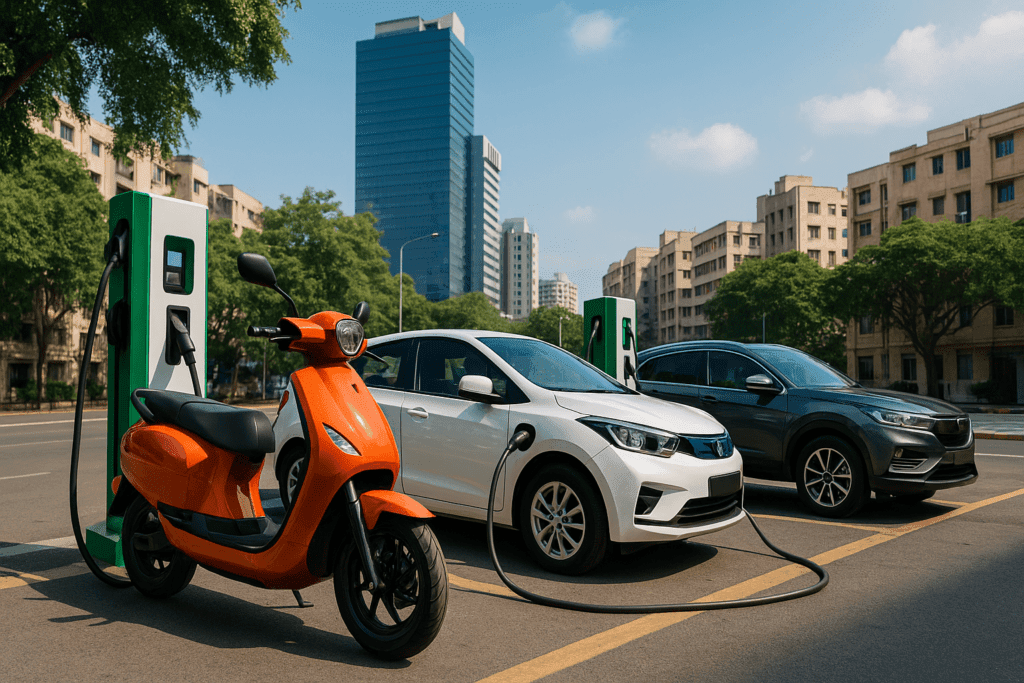
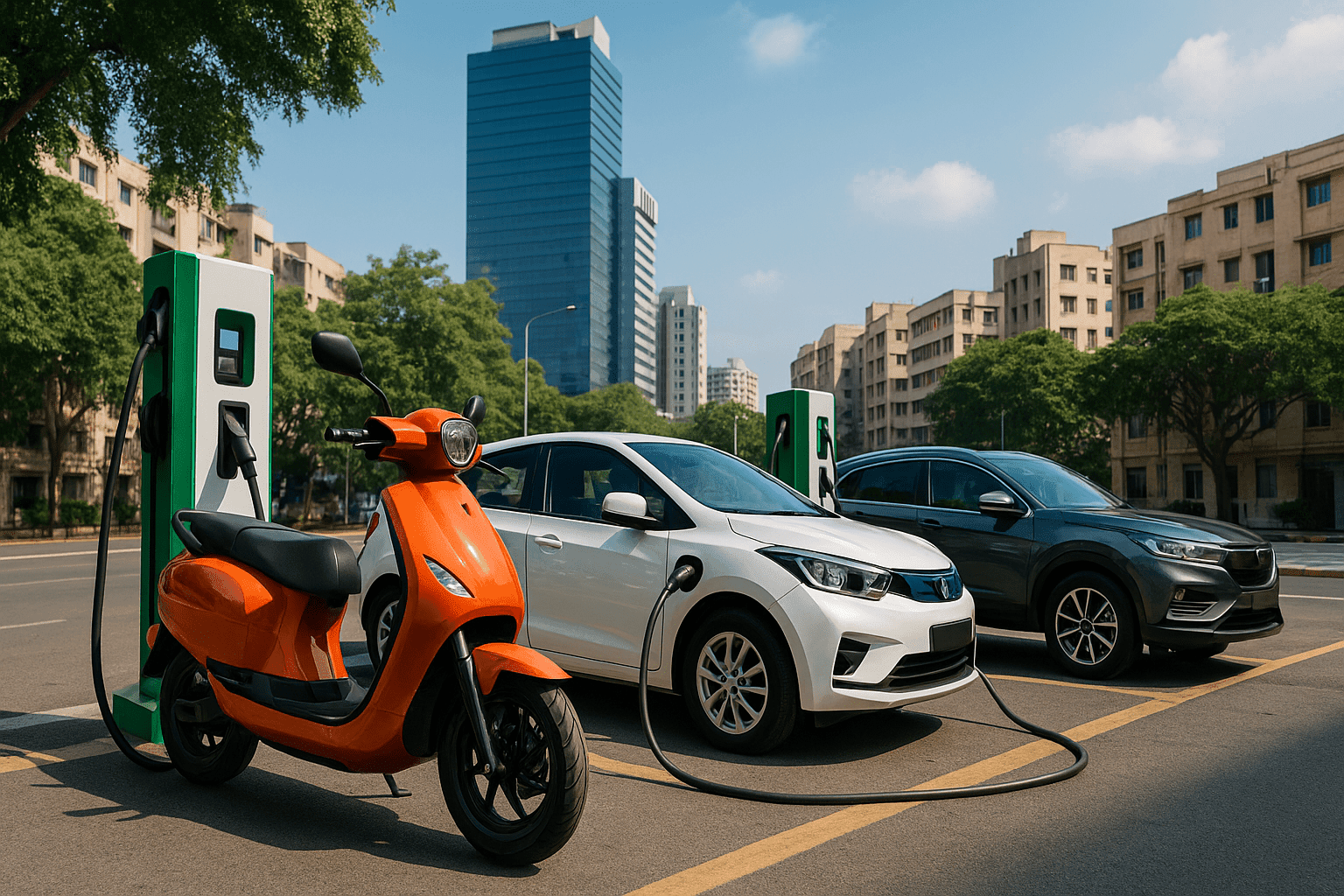
Electric vehicles in India are transforming the country’s automobile industry as consumers, manufacturers, and policymakers increasingly shift toward sustainable mobility solutions. What was once considered a niche segment has now become a central pillar of India’s long-term transport and energy strategy.
Rising fuel prices, environmental concerns, and strong government incentives have collectively accelerated the adoption of electric mobility. From two-wheelers and passenger cars to commercial fleets and public transport, electric vehicles are steadily gaining ground across multiple segments.
Electric Vehicles in India Gain Momentum Across Segments
Electric vehicles in India have witnessed consistent growth, particularly in the two-wheeler segment, which accounts for the largest share of total EV sales. Urban commuters are increasingly opting for electric scooters and motorcycles due to lower running costs, ease of charging, and supportive state-level incentives.
Passenger electric cars are also gaining traction as driving ranges improve and charging infrastructure expands. Automakers are launching new models across price points, targeting both mass-market buyers and premium consumers.
Commercial and Fleet Adoption Expands
Fleet operators and logistics companies are playing a crucial role in accelerating EV adoption. Electric three-wheelers and delivery vans are increasingly being deployed for last-mile connectivity, especially in urban areas.
Experts note that predictable routes and lower operational costs make electric vehicles particularly suitable for commercial use. Ride-hailing platforms and e-commerce firms are also committing to electrification targets, further boosting demand.
Policy Support Strengthens EV Ecosystem
Government policy has been a major catalyst for the rise of electric vehicles in India. Central schemes and state-level incentives have helped reduce upfront costs and encouraged manufacturers to invest in electric mobility.
Subsidies, tax benefits, and reduced registration fees have made EVs more accessible to consumers. Additionally, localization policies are encouraging domestic manufacturing of batteries and components, reducing reliance on imports.
According to policy frameworks outlined by NITI Aayog, electric mobility is critical for reducing oil imports and lowering carbon emissions in the transport sector.
Charging Infrastructure Expands Nationwide
One of the key challenges for electric vehicles in India has been charging availability. However, significant progress is being made as both public and private players invest in charging infrastructure across cities and highways.
Fast-charging stations are being deployed along major transport corridors, while residential and workplace charging solutions are becoming more common. Automakers are also partnering with energy companies to offer bundled charging solutions to customers.
Battery Technology and Cost Trends
Advancements in battery technology are gradually improving driving range and reducing charging time. While battery costs remain a concern, economies of scale and domestic production are expected to bring prices down over time.
Industry analysts believe that battery innovation will play a decisive role in determining the pace of EV adoption over the next decade.
Automakers Restructure Strategies Around EVs
Traditional automobile manufacturers are restructuring long-term strategies to accommodate electric vehicles. Several companies have announced dedicated EV platforms and committed significant capital to electric research and development.
Startups are also emerging as strong competitors, particularly in the two-wheeler and three-wheeler segments. This competitive landscape is driving innovation and expanding consumer choice.
At the same time, legacy automakers are balancing the transition by maintaining internal combustion engine production while gradually increasing EV capacity.
Challenges That Remain for Electric Mobility
Despite rapid growth, electric vehicles in India face challenges that could slow adoption if not addressed. High upfront costs, limited charging access in smaller towns, and concerns about battery lifespan remain key issues.
There is also a need for skilled technicians and service infrastructure to support EV maintenance. Policymakers and industry stakeholders are increasingly focusing on workforce training and standardisation to address these gaps.
Grid Readiness and Energy Supply
As EV adoption rises, electricity demand is expected to increase. Experts stress the importance of strengthening grid infrastructure and expanding renewable energy capacity to ensure sustainable charging solutions.
Integrating EVs with renewable power sources could further enhance the environmental benefits of electric mobility.
Long-Term Outlook for Electric Vehicles in India
Looking ahead, electric vehicles in India are expected to play a central role in the country’s transportation future. Analysts predict steady growth across segments as technology matures and infrastructure improves.
With continued policy support, industry investment, and consumer awareness, electric mobility is likely to reshape India’s automobile industry over the coming years. The transition, while gradual, appears irreversible as sustainability becomes a core priority.