Google’s Quantum Computing Revolution: Inside the Willow Chip Breakthrough
How Google’s Latest Quantum Computer is Reshaping Technology’s Future
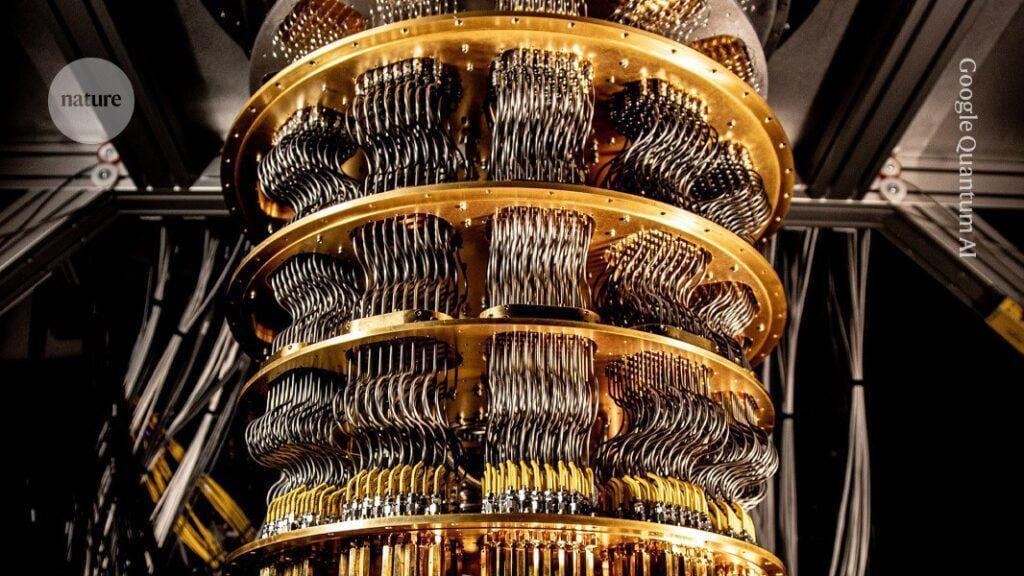
The quantum computing landscape experienced a seismic shift with Google’s announcement of groundbreaking achievements using its Willow quantum chip. This development represents not just an incremental improvement but a fundamental leap forward in humanity’s quest to harness the bizarre properties of quantum mechanics for practical computation.
Understanding the Google Quantum Computer Journey
Google’s quantum computing endeavor began years ago with ambitious goals to create machines that could solve problems beyond the reach of classical computers. The tech giant’s quantum computing division, Google Quantum AI, has consistently pushed boundaries in this cutting-edge field.
The journey started gaining significant attention in 2019 when Google announced its Sycamore quantum computer achieved “quantum supremacy” – demonstrating that a quantum system could perform a specific calculation faster than the world’s most powerful supercomputers. The Google quantum computer Sycamore featured 53 qubits and completed a task in 200 seconds that would have taken classical supercomputers approximately 10,000 years.
However, Sycamore was just the beginning. Google’s researchers recognized that achieving practical quantum computing required overcoming a critical obstacle: quantum error correction.
Enter Willow: Google’s Game-Changing Quantum Chip
In December 2024, Google unveiled Willow, a state-of-the-art quantum processor that addresses one of quantum computing’s most persistent challenges. The Google quantum computer Willow represents a paradigm shift in how quantum systems handle errors.
Willow is a 105-qubit superconducting quantum computing processor manufactured in Santa Barbara, California, and it achieved something revolutionary: it can reduce errors exponentially as it scales up using more qubits, cracking a challenge that has plagued the field for nearly three decades.
Traditional quantum computers faced a paradoxical problem – adding more qubits typically increased errors rather than computational power. Google claims to have turned that on its head, adding qubits to Willow to correct errors instead.
The Mind-Bending Performance Benchmark
The Google quantum chip Willow demonstrated jaw-dropping computational capabilities. Willow performed a computation in under five minutes that would take one of today’s fastest supercomputers 10 septillion years – a timespan that vastly exceeds the age of the universe itself.
This astronomical performance difference comes from the fundamental way quantum computers process information. While classical computers work with bits that are either 0 or 1, Google quantum computer qubits exist in quantum superposition, simultaneously representing multiple states. This allows quantum systems to explore vast solution spaces that would be impossible for traditional computers.
The Quantum Echoes Algorithm: Pushing Toward Real-World Applications
Building on Willow’s hardware achievements, Google recently announced another breakthrough: the Quantum Echoes algorithm. The algorithm ran 13,000 times faster than possible on the world’s best supercomputer, and crucially, it’s verifiable – meaning it can be repeated on other quantum computers to confirm results.
The Quantum Echoes algorithm can be useful in learning the structure of systems in nature, from molecules to magnets to black holes. This represents the first practical algorithm demonstrating quantum advantage with real-world scientific applications, moving beyond abstract benchmarking exercises.
The algorithm works like sophisticated sonar, sending carefully crafted signals through quantum systems and listening for amplified echoes that reveal hidden information about molecular structures and physical properties.
How Google Quantum Computer Qubits Function
Google’s Quantum, At the heart of every Google quantum computer lie qubits – quantum bits that leverage the strange properties of quantum mechanics. Google’s approach uses superconducting circuits that function as “artificial atoms” operating at temperatures colder than outer space.
The current-generation Willow chip features fidelities of 99.97% for single-qubit gates, 99.88% for entangling gates, and 99.5% for readout, representing industry-leading precision. These specifications might seem like minor percentages, but in quantum computing, such accuracy levels are essential for maintaining quantum coherence and performing reliable calculations.
Real-World Applications on the Horizon
Google envisions transformative applications for its quantum computers across multiple sectors. Potential applications include helping design drugs with more certainty about how they’d interact with a disease, running better simulations of new battery technology, and potentially helping design nuclear fusion reactors.
Pharmaceutical companies could use quantum simulations to model complex molecular interactions that are computationally intractable today. Energy researchers could optimize battery chemistry and grid management. Artificial intelligence systems could potentially leverage quantum acceleration for training advanced models.
Google scientists predict that practical applications only possible with quantum computers could emerge within five years, though this timeline depends on successfully scaling systems to millions of qubits.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
Google’s Quantum,Despite remarkable progress, experts caution that significant challenges remain. Current quantum systems still operate in what researchers call the “noisy intermediate-scale quantum” era. Achieving fault-tolerant quantum computing capable of solving commercially relevant problems requires continued hardware improvements and much larger qubit arrays.
The Google quantum computer name Willow marks a milestone, but it’s one chapter in a longer story. As quantum error correction improves and systems scale, we’re moving closer to a future where quantum and classical computers work together, each handling the problems they’re best suited to solve.
Conclusion: A Quantum Leap Forward
Google’s achievements with the Willow quantum chip and Quantum Echoes algorithm represent more than technical accomplishments – they demonstrate that practical quantum computing is transitioning from theoretical possibility to emerging reality. While fully functional, large-scale quantum computers remain years away, the trajectory is clear: we’re entering an era where quantum mechanics will augment human problem-solving capabilities in unprecedented ways.
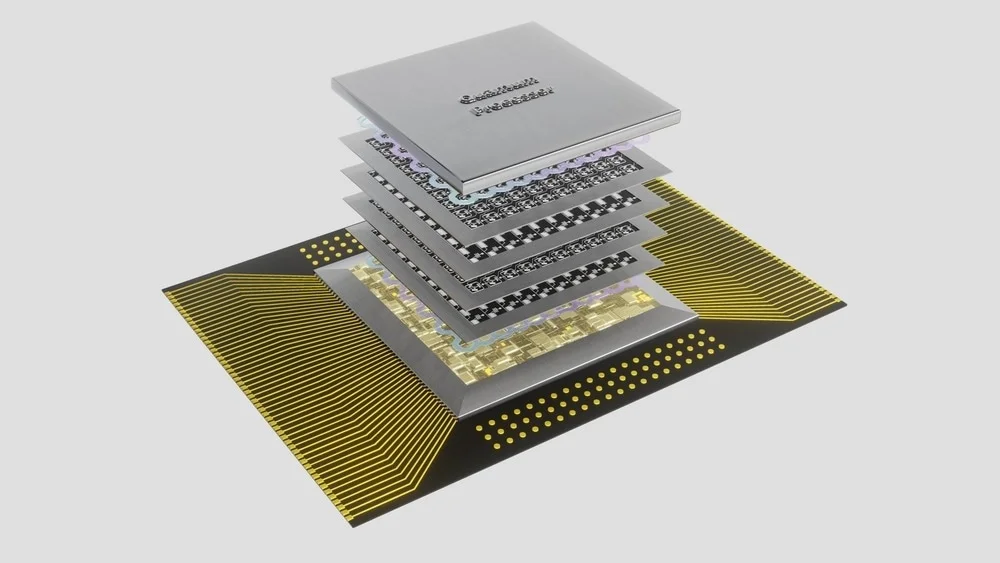
The complete information of Google’s Quantum is available on official website